Monday, October 31, 2011
2.68b Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation : osmosis + control
By controlling the salt and water in the blood the Kidney can keep the blood isotonic (optimum) with the cells cytoplasm, therefore maintaining function of the cells.
2.68a Excretion
The kidney (and liver) and the excretion of Urea (carries potentially toxic hydrogen)
(the filtered blood - free of urea - travels back)
(the filtered blood - free of urea - travels back)
2.67b Human Organs of Excretion
1. Lung
- carbon dioxide (from respiration)
2. Kidney
- Water
- Urea (amino acids)
- Salts
3. Skin
- Through sweat : water, salts
- Small amount of Urea
- carbon dioxide (from respiration)
2. Kidney
- Water
- Urea (amino acids)
- Salts
3. Skin
- Through sweat : water, salts
- Small amount of Urea
3.67a Excretion in Plants
1. Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water ---> glucose + oxygen
- oxygen is a waste molecule and therefore excreted
2. Respiration
glucose + oxygen ---> ATP + carbon dioxide + water
- Carbon dioxide in a waste molecule and therefore excreted
carbon dioxide + water ---> glucose + oxygen
- oxygen is a waste molecule and therefore excreted
2. Respiration
glucose + oxygen ---> ATP + carbon dioxide + water
- Carbon dioxide in a waste molecule and therefore excreted
Sunday, October 9, 2011
3.34 Causes of Mutation
1. Radiation e.g x-rays
sunshine (UV Rays ) > skin cancer
2. Chemicals e.g Tars (tobacco) > cancer
Chemicals which cause mutations are called, Mutages.
Chemicals that cause cancer are called Carcinogens.
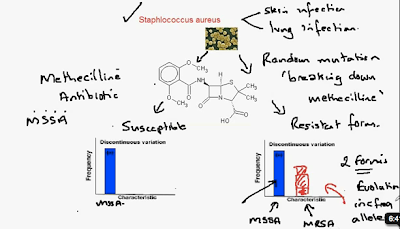
3.33 Antibiotic Resistance
As the resistant from increasingly survives over time, it becomes more common
Meaning the antibiotic no longer works
3.31 Evolution
Evolution : change in the form of organisms (new forms)
: change in the frequency (number) of alleles
: increase in the frequency of the alleles for resistance
Natural Selection : Mechanism of evolution
: change in the frequency (number) of alleles
: increase in the frequency of the alleles for resistance
Natural Selection : Mechanism of evolution
3.30 Mutation
The change (mutation) creates a new version of the allele
Can affect: phenotype, production of protein
Mutation, changes base sequence
3.29 Species Variation
Variation = see-able differences in phenotype
Individual Phenotype = Genotype + Environment
Vpop = Vgeno + Venvironment
1. Vpop = Vgeno (no environmental impact)
e.g bloodgroup
2. Vpop = Vgeno + Vpop
e.g height
3. Vpop = Venvironment (no genotypic influence)
e.g home language
Individual Phenotype = Genotype + Environment
Vpop = Vgeno + Venvironment
1. Vpop = Vgeno (no environmental impact)
e.g bloodgroup
2. Vpop = Vgeno + Vpop
e.g height
3. Vpop = Venvironment (no genotypic influence)
e.g home language
Sunday, October 2, 2011
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)